Understanding Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM remains one of the most vital components of any computing device, from desktops and laptops to smartphones and tablets.

Random Access Memory (RAM) is a fundamental component in computing, serving as the system’s short-term memory where data is temporarily stored for quick access. The choice of RAM significantly impacts system performance, affecting everything from multitasking capabilities to gaming and software execution speeds. Over the years, RAM technology has evolved, leading to notable improvements in speed, efficiency, and overall computing experience.
What is RAM and Why is It Important?
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of computer memory that stores data temporarily for quick access by the processor. Unlike permanent storage devices like hard drives or SSDs, RAM holds information that the system actively uses, making it crucial for fast performance and multitasking.
When you open an application, your operating system loads its necessary data into RAM, allowing the processor to quickly access and modify it. More RAM means the system can handle multiple tasks simultaneously without slowing down. If RAM is insufficient, the computer relies on slower storage, causing lag and reduced efficiency.
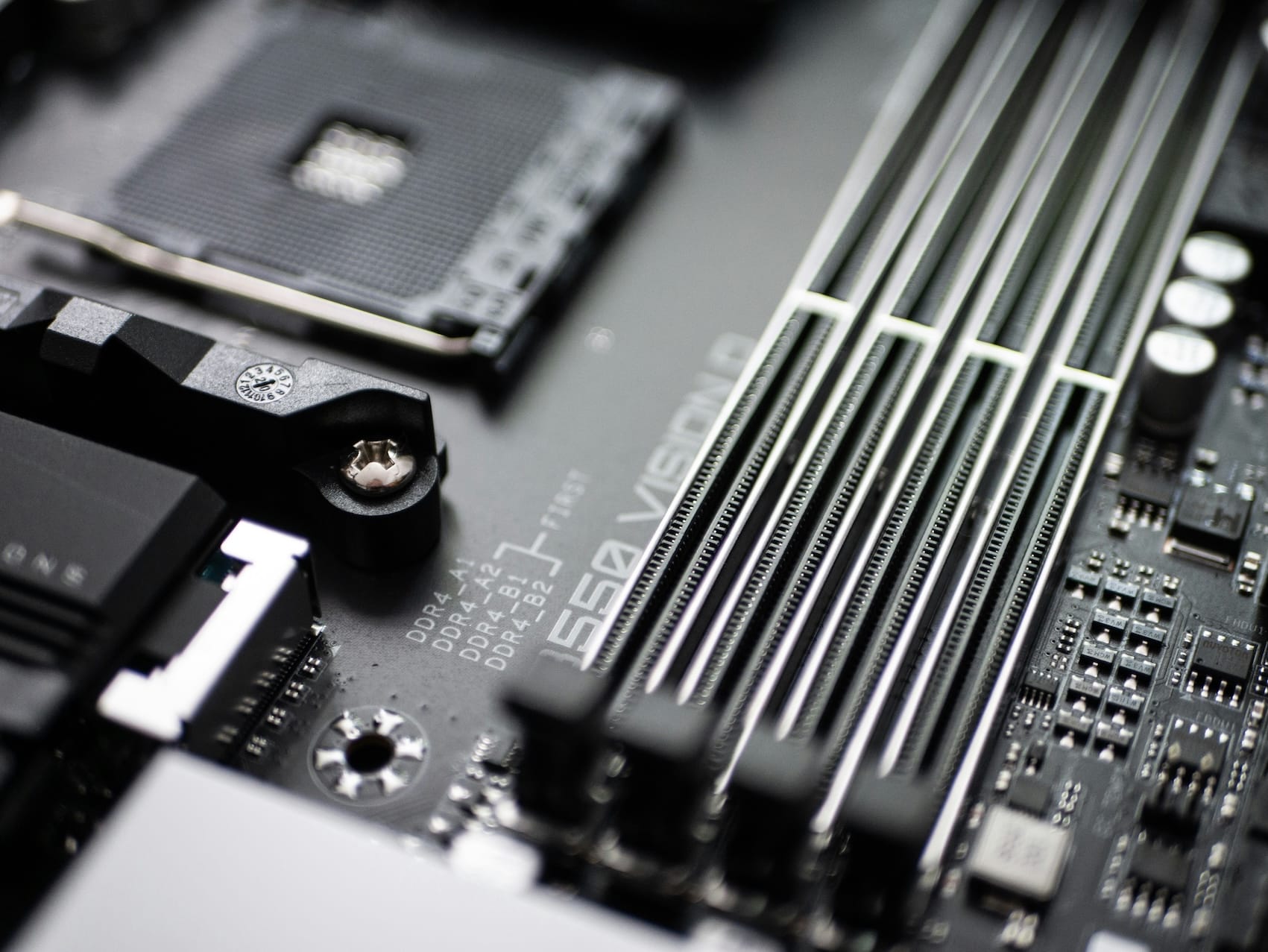
Modern RAM comes in different generations, such as DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5, each offering higher speeds, lower power consumption, and better bandwidth. DDR5, the latest standard, significantly improves data transfer rates, making it ideal for gaming, content creation, and AI applications.
Choosing the right RAM capacity and speed ensures a smooth computing experience, whether for casual use, gaming, or professional workloads. As programs and operating systems become more demanding, having ample RAM is essential to maintaining fast and responsive performance.
Key Functions of RAM:
- Multitasking: More RAM allows users to run multiple applications without system lag.
- Gaming Performance: High-speed RAM enhances frame rates and reduces stuttering.
- Software Efficiency: Intensive applications like video editing and 3D rendering require significant RAM for seamless operation.
Inadequate RAM results in sluggish performance, application freezes, and reduced productivity. Choosing appropriate RAM capacity and speed ensures a responsive and efficient computing experience.
Evolution of RAM: DDR5 vs DDR4 vs DDR3
Over the years, RAM technology has evolved significantly, with each new generation bringing higher speeds, better efficiency, and improved reliability. DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 represent key milestones in this progression, offering enhanced data transfer rates and reduced power consumption. While DDR3 served as the foundation for high-speed computing, DDR4 became the dominant standard with increased bandwidth and stability. DDR5, the latest iteration, takes performance to new heights, doubling bandwidth while optimising power efficiency thereby making it ideal for gaming, AI workloads, and data centers.
DDR3 RAM: The Legacy Standard
DDR3, introduced in 2007, was widely used for over a decade. It provided a notable leap in speed over DDR2 but is now considered outdated due to lower bandwidth and higher power consumption.
- Speed: Ranges from 800 MHz to 2133 MHz
- Power Consumption: 1.5V (with low-power variants at 1.35V)
- Data Rate: Single-channel architecture with 64-bit bandwidth
- Limitations: Struggles with modern workloads, lacks efficiency optimizations
While DDR3 still exists in legacy systems, it is largely phased out in favor of DDR4 and DDR5.
DDR4 RAM: The Modern Workhorse
DDR4 was launched in 2014, bringing improvements in speed and efficiency. It remains the standard choice for most gaming PCs, workstations, and laptops.
- Speed: 2133 MHz to 3200 MHz, reaching higher with overclocking
- Power Consumption: 1.2V (lower than DDR3, increasing energy efficiency)
- Data Rate: Increased bandwidth, supporting dual-channel configurations
- Improved Latency & Stability: Better signal integrity for reliable computing
DDR4’s higher speeds and lower voltage make it ideal for high-performance tasks. However, DDR5 brings further advancements.
DDR5 RAM: The Next Generation
DDR5, introduced in 2021, is the latest iteration designed to push performance to new levels. It doubles bandwidth while improving power efficiency.
- Speed: 4800 MHz to 8400 MHz (significantly faster than DDR4)
- Power Consumption: 1.1V (even lower than DDR4)
- Data Rate: Up to twice the bandwidth of DDR4, allowing faster data transfer
- ECC (Error Correction Code): Improved reliability with built-in data correction
DDR5 not only enhances gaming and high-performance computing, but also optimizes efficiency for data centers and AI workloads.
Choosing the Right RAM: Why It Matters
Selecting the correct RAM depends on several factors. Here’s your information formatted with bullet points for clarity:
1. Workload Requirements
- Basic computing: 8GB DDR4
- Gaming & multitasking: 16GB DDR4 or DDR5
- Professional tasks (video editing, 3D rendering): 32GB+ DDR5
2. Compatibility
- Check motherboard support—some older systems are limited to DDR3 or DDR4
- Ensure RAM speed aligns with CPU capability
3. Future-Proofing
- If building a new system, opting for DDR5 ensures long-term usability
- For budget-conscious users, DDR4 remains a strong choice
4. Power Efficiency
- Lower voltage RAM (DDR5) benefits laptops and energy-efficient setups
Difference Between RAM in Computers vs Smartphones
While RAM (Random Access Memory) serves the same fundamental purpose in computers and smartphones—providing temporary storage for fast data access—it is optimized differently for each device due to their unique operating environments.
1. Architecture & Usage
- Computer RAM: In desktops and laptops, RAM is upgradable and replaceable, usually connected via DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) slots on the motherboard. It supports higher speeds and works alongside dedicated GPUs for gaming or professional workloads.
- Smartphone RAM: Mobile devices use LPDDR (Low-Power DDR) RAM, which is soldered onto the motherboard for energy efficiency. LPDDR prioritizes low power consumption, crucial for battery life, and integrates tightly with system-on-chip (SoC) designs.
2. Power Efficiency
- Computer RAM: Requires more power (~1.2V for DDR4, 1.1V for DDR5) but benefits from a direct power supply.
- Smartphone RAM: Uses LPDDR technology (e.g., LPDDR5) with lower voltage (~0.5V–1V) to extend battery life.
3. Multitasking Needs & Optimization
- Computers: Rely on higher bandwidth RAM and swap data with storage drives if needed.
- Smartphones: Since phone apps stay active in the background, devices optimize RAM usage differently, often using aggressive memory compression to keep apps ready.
Why Do Smartphones Have More RAM Compared to Laptops?
Modern smartphones often advertise higher RAM amounts (e.g., 12GB–16GB in flagship models), which may seem excessive compared to many laptops with 8GB–16GB RAM. This is due to several key reasons:
- Apps Stay Running in the Background
Unlike laptops, which swap inactive programs to storage, smartphones keep apps in memory to provide a smooth multitasking experience. This requires more RAM to prevent apps from reloading. - Less Swap Memory (Virtual RAM)
Laptops can offload memory-intensive processes to SSD/HDD swap space, but smartphones lack large swap storage, making more physical RAM necessary. - Heavy Custom UI & Features
Many Android smartphones have resource-heavy UI skins (such as Samsung’s One UI or Xiaomi’s MIUI), consuming extra RAM compared to a lightweight Windows or macOS system. - Gaming & AI Features
Smartphones now handle high-end gaming, AI processing, and camera enhancements, demanding more RAM for real-time performance.
Both computers and smartphones use RAM for fast data access, but mobile devices require efficient, low-power memory that supports always-active apps and battery optimization. While laptops and desktops rely on high-speed DDR4/DDR5 RAM, smartphones prioritize LPDDR RAM with larger capacities to maintain smooth multitasking and advanced features.
Conclusion
RAM remains one of the most vital components of any computing device, from desktops and laptops to smartphones and tablets. As technology evolves, newer RAM generations—like DDR5—offer higher speeds, lower power consumption, and improved efficiency, enabling seamless multitasking, gaming, and professional workloads. While desktop and laptop RAM prioritizes raw performance and upgradability, smartphone RAM focuses on power efficiency and continuous app retention, ensuring a smooth user experience in mobile environments. The increasing RAM capacities in modern smartphones underscore the need for efficient multitasking, demanding more physical memory than laptops with expandable storage solutions.
Understanding RAM specifications and choosing the right capacity based on personal computing needs ensures long-term system performance and reliability. Whether upgrading an old system or building a new one, selecting the right RAM can dramatically enhance productivity, speed, and overall user experience.




