Lifespan and Degradation of Lithium-Ion Batteries
While their lifespan typically ranges from 500 to 1000 charge cycles, natural aging, chemical wear, heat exposure, and deep discharges cause degradation over time.

Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries power most of our modern devices, from laptops and smartphones to electric vehicles and wearable gadgets. Despite their efficiency, these batteries degrade over time, leading to reduced battery life and faster discharge rates in older devices. This article explores how Li-ion batteries age, why laptops and phones lose battery life over years of usage, and how Apple devices track battery health, including charge cycles and degradation.
How Long Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Last?
The lifespan of a Li-ion battery is usually measured in charge cycles rather than years. A charge cycle occurs when a battery discharges and recharges completely. Most modern lithium-ion batteries last between 300 and 1000 charge cycles, depending on usage patterns, temperature exposure, and charging habits.
Battery Lifespan by Device Type
- Smartphones: Around 500–800 cycles, typically lasting 2–3 years before noticeable degradation.
- Laptops: Around 800–1000 cycles, usually 3–5 years of optimal performance before serious wear.
- Electric Vehicles: Can reach 1000+ cycles, thanks to advanced thermal management systems.
After hundreds of cycles, batteries lose their ability to hold a full charge, leading to shorter runtime and faster discharge rates.
Why Do Batteries Lose Charge Faster Over Time?
Aging lithium-ion batteries gradually hold less charge and discharge faster due to several factors such as:
1. Chemical Aging
Li-ion batteries rely on chemical reactions to store and release energy. Over time, these reactions cause:
- Loss of lithium ions, reducing energy storage capacity.
- Electrode wear, leading to internal resistance buildup.
- Formation of Solid Electrolyte Interface (SEI), which slows charge flow.
2. Increased Internal Resistance
As batteries degrade, their internal resistance rises, meaning they lose energy even when idle. This explains why old smartphones and laptops drain quickly even in standby mode.
3. Heat and Temperature Damage
Excessive heat accelerates degradation by damaging battery cells.
- Frequent overheating due to gaming or high-performance usage shortens lifespan.
- Extreme cold also reduces battery efficiency.
Apple devices include thermal management systems to prevent overheating, but sustained high temperatures will still degrade battery health.
4. Deep Discharges and Overcharging
Allowing a battery to drain completely to 0% too often, or consistently charging it to 100%, wears it out faster. Modern batteries perform best when kept between 20–80% charge levels.
Battery Charge Cycles in Apple Devices
Apple monitors battery cycles in iPhones, MacBooks, and iPads to estimate battery health.
What Are Battery Charge Cycles?
- A cycle occurs when a battery discharges 100%, either in one go or over multiple charges.
- Example: If an iPhone is charged from 50% to 100% twice, it counts as one charge cycle (50% + 50% = 100%).
- MacBooks generally last 1000 cycles, while iPhones range from 500–800 cycles before battery health declines.
To check battery cycles in a MacBook:
- Click Apple menu → About This Mac → System Report.
- Navigate to Power → Look for Battery Cycle Count.
To check battery health in an iPhone:
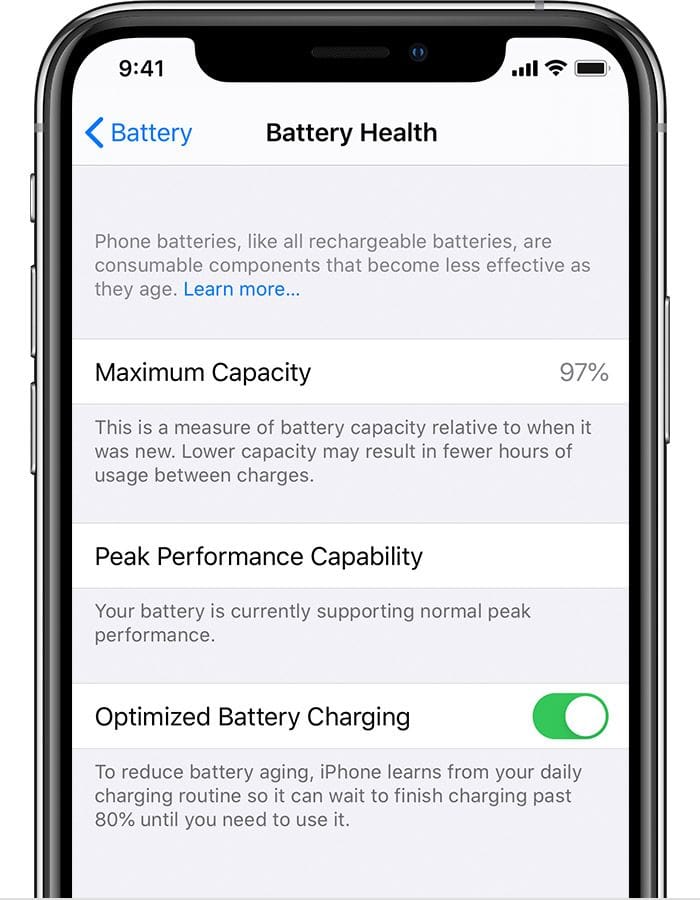
- Go to Settings → Battery → Battery Health & Charging.
- You’ll see the maximum capacity (%) left. A lower percentage means degraded health.
What Does “Battery Health” & "Maximum Capacity" Mean in iPhones and MacBooks?
Apple devices display Battery Health, a metric reflecting remaining battery capacity compared to when it was new.
Battery Health on iPhones
- A new iPhone has 100% battery health.
- After 500 cycles, it may drop to 80–85%, leading to shorter charge retention.
- Below 80%, peak performance capability might reduce, causing slower processing speeds.
Battery Health on MacBooks
- MacBooks typically last 1000 cycles, but battery health declines gradually.
- At 80% or lower, noticeable charge drain occurs.
Apple uses Optimized Battery Charging to slow degradation by reducing time spent at full charge. If enabled, the device learns your routine and limits charging beyond 80% until needed.
Maximum Capacity
Maximum Battery Capacity in Apple devices refers to the remaining energy-holding capability of the battery compared to when it was new. It is displayed as a percentage in iPhones and MacBooks under the Battery Health & Charging section. How It Works:
- When a device is new, the maximum battery capacity is 100%, meaning it holds full charge as intended.
- Over time, due to charge cycles, chemical aging, and wear, this capacity declines.
- If an iPhone shows 85% maximum capacity, it means the battery can only store 85% of its original full charge, leading to shorter usage time per charge.
- Below 80%, Apple may reduce peak performance to prevent unexpected shutdowns.
- MacBooks and iPhones with degraded batteries discharge faster and require more frequent charging.
Apple devices use Optimised Battery Charging to slow down degradation by reducing full charges to 100% too often. Would you like guidance on checking battery capacity on your device?
Maintaining 100% Battery Health
Maintaining 100% battery health in Apple devices for the long term is challenging because lithium-ion batteries naturally degrade with use. However, you can slow down battery wear and maximise longevity by following these best practices:
1. Avoid Frequent Full Charges (0%–100%)
- Li-ion batteries last longer when kept between 20% and 80% charge.
- Don’t let the battery drain to 0% often, as deep discharges accelerate degradation.
- Unplug once you reach 80–90%, avoiding prolonged 100% charge levels.
2. Use Optimized Charging (Apple’s Built-in Feature)
- iPhones & MacBooks use Optimized Battery Charging, which delays charging past 80% until needed.
- Enable it in Settings > Battery > Battery Health & Charging to reduce stress on the battery.
3. Avoid Overheating and Extreme Cold
- Heat damages battery cells, reducing capacity faster.
- Avoid gaming or heavy usage while charging, as it generates excess heat.
- Store devices between 10°C and 35°C—extreme cold also affects charge retention.
4. Use Certified Chargers & Cables
- Always use Apple-certified chargers or reputable brands that match voltage standards.
- Cheap, third-party chargers may deliver unstable power, harming battery longevity.
5. Don’t Keep Your Device Plugged in Constantly
- MacBooks handle continuous charging better, but it’s best to unplug periodically if not actively using them.
- For iPhones, charge in smaller increments rather than overnight charging daily.
6. Store Devices at Proper Charge Levels
- If storing an iPhone/MacBook for weeks/months, keep charge around 50%.
- Don’t store devices at 0% charge, as batteries may enter deep discharge mode, making them harder to recover.
7. Monitor Battery Health & Cycle Count
- Check battery cycles (MacBook: System Report > Power; iPhone: Settings > Battery Health).
- If battery health drops below 80%, performance throttling may begin.
While 100% battery health won’t last forever due to natural wear, following these tips can keep your Apple device’s battery in excellent condition for years. Careful charging habits, temperature management, and using official accessories all contribute to extending battery lifespan significantly.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries are essential to modern technology, powering smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices. While their lifespan typically ranges from 500 to 1000 charge cycles, natural aging, chemical wear, heat exposure, and deep discharges cause degradation over time. Apple devices help users track battery health through charge cycle monitoring and optimised charging features, ensuring prolonged battery efficiency. However, no battery lasts forever, and users must adopt best charging practices to maintain peak performance for as long as possible.
By following simple habits like keeping charge levels between 20–80%, avoiding excessive heat, and using certified accessories, users can slow degradation and maximize battery life. While battery capacity will inevitably decline, smart maintenance ensures a longer-lasting and more efficient device experience.






